Keto Diet:
14 June 2023Unlocking the Power of Ketosis
Ketosis is a metabolic state that occurs when the body shifts from primarily using glucose (from carbohydrates) as its fuel source to using ketones (from fat) as an alternative fuel source. In a typical diet, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then used by the body for energy production. However, when carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, such as in the case of the ketogenic diet, the body enters a state of ketosis.
During ketosis, the liver converts stored fat into ketones through a process called ketogenesis. Ketones, specifically beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), acetoacetate, and acetone, are released into the bloodstream and serve as an alternative energy source for cells throughout the body, including the brain.
The key principle of the ketogenic diet is to restrict carbohydrates to a very low level, usually below 50 grams per day, or approximately 5-10% of total caloric intake. This reduction in carbohydrates forces the body to rely on stored fat for fuel. By consuming a moderate amount of protein and a high amount of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and oils, individuals on a ketogenic diet maintain a state of ketosis.
In ketosis, the body undergoes a metabolic adaptation utilizing fat as its primary fuel source instead of glucose.
This shift has several effects on the body, including:
- Increased Fat Burning: The body breaks down stored fat into fatty acids and converts them into ketones, which are then used for energy. This can lead to efficient fat loss and weight management.
- Reduced Insulin Levels: With limited carbohydrate intake, the body requires less insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. This can be beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
- Appetite Suppression: The consumption of healthy fats and moderate protein on the ketogenic diet can help promote satiety and reduce cravings, leading to potential appetite control.
- Stable Energy Levels: Ketones provide a stable and sustained energy source for the body. Many individuals report improved mental focus and sustained energy levels while in ketosis.
It’s important to note that the ketogenic diet requires careful monitoring and should be followed under the guidance of a healthcare professional or registered dietitian. It may not be suitable for everyone, and individual responses to the diet can vary.
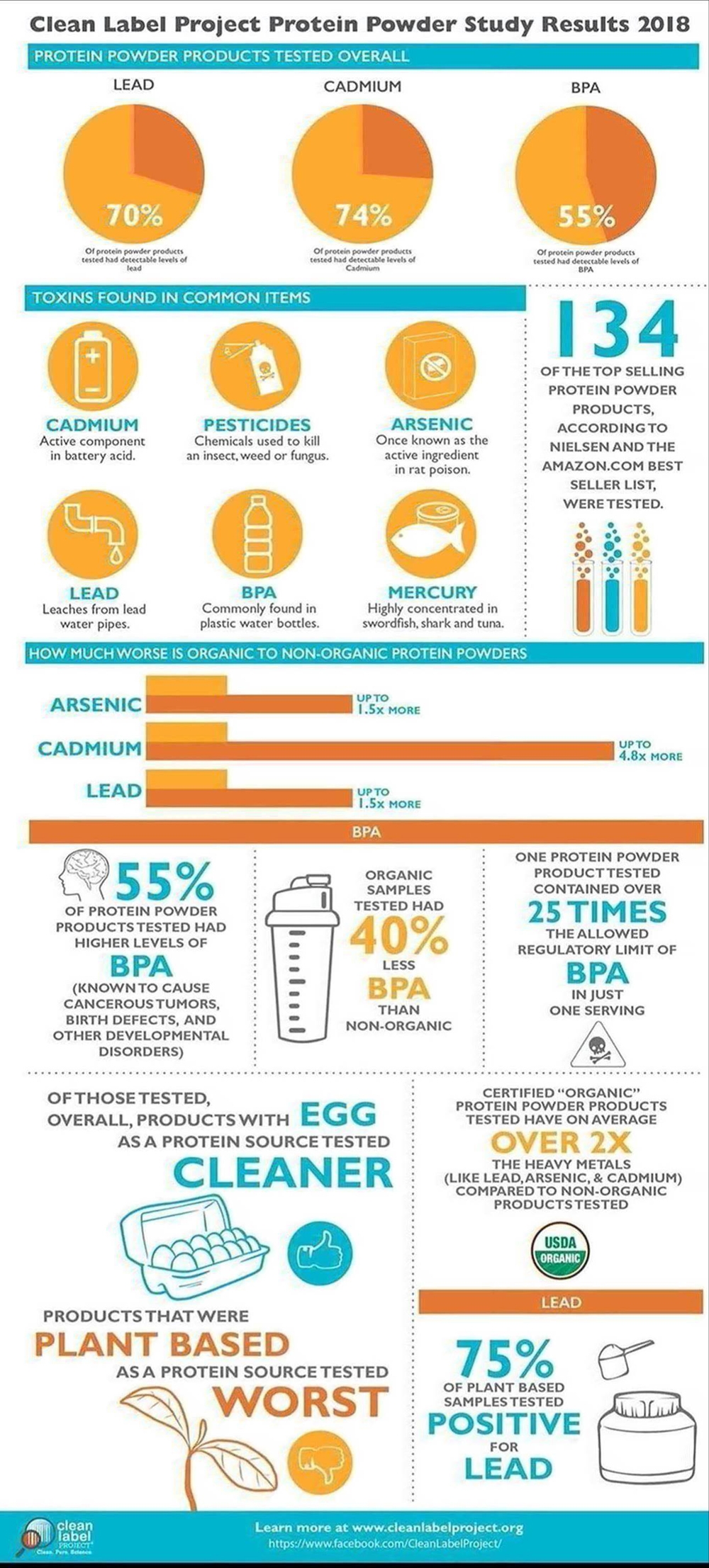
Here are some common supplements that individuals following a ketogenic diet may consider:
- Electrolytes: When following a ketogenic diet, there can be an increased risk of electrolyte imbalances due to reduced carbohydrate intake and increased water loss. Supplementing with electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium can help maintain proper electrolyte balance.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The ketogenic diet is often high in saturated fats, and it’s important to maintain a balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil or algae-based supplements, can help achieve this balance and support heart health.
- MCT Oil: Medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) oil is a type of fat that is rapidly converted into ketones by the liver. Adding MCT oil to your diet can provide a quick source of ketones and help maintain ketosis. It can be used as an ingredient in cooking or added to beverages like coffee or smoothies.
- Exogenous Ketones: Exogenous ketones are supplemental ketones that can be consumed to elevate blood ketone levels. They can be in the form of ketone salts or ketone esters. Exogenous ketones may help support energy levels and aid in transitioning into ketosis. However, they are not necessary for everyone and should be used with caution.
- Fiber Supplements: Since the ketogenic diet tends to be low in fiber due to limited carbohydrate intake, it’s important to ensure an adequate fiber intake for gut health and regular bowel movements. Fiber supplements such as psyllium husk or glucomannan can help meet the recommended daily fiber intake.
Here are a few key areas of research on ketosis:
- Ketosis and Weight Loss: Numerous studies have investigated the effects of ketosis on weight loss and body composition. Research has examined the metabolic changes associated with the ketogenic diet, including increased fat burning and improved satiety, which may contribute to weight loss.
- Ketosis and Diabetes Management: Some studies have explored the potential benefits of ketosis in managing type 2 diabetes. Research has examined the impact of the ketogenic diet on blood glucose control, insulin sensitivity, and markers of metabolic health in individuals with diabetes.
- Ketosis and Neurological Disorders: Ketosis has been studied for its potential therapeutic effects on neurological disorders such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and traumatic brain injury. Research has investigated the impact of ketone bodies on brain function and neurological outcomes.
- Ketosis and Athletic Performance: Several studies have explored the effects of ketosis on athletic performance and endurance. Research has investigated adaptations to fat metabolism, glycogen utilization, and performance outcomes in athletes following a ketogenic diet.
- Ketosis and Metabolic Health: Research has examined the effects of ketosis on various metabolic markers, including lipid profiles, blood pressure, inflammation, and markers of cardiovascular health. Some studies suggest potential improvements in these areas, but more long-term research is needed.